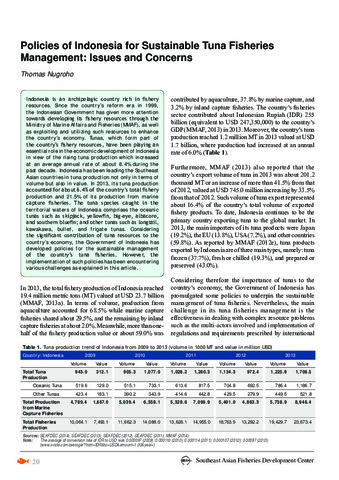
| dc.contributor.author | Kikawa, Shoji | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2018-11-19T03:50:29Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2018-11-19T03:50:29Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1977 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Kikawa, S. (1977). Tuna and tuna-like fish resources in the South China Sea and adjacent waters. In Proceedings of the Technical Seminar on South China Sea Fisheries Resources, Bangkok, Thailand, 21-25 May 1973 (pp. 31-41). Tokyo, Japan: Japan International Cooperation Agency. | en |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12066/4127 | |
| dc.description.abstract | The distribution of tunas and billfishes in the South China Sea and the Southeast Asian waters was shown on the commercial longline data.
The seasonal changes in the hook-rate and the size composition of the yellowfin and bigeye tuna in the South China Sea were given and the previous suppositions on their stock structures in adjacent areas, the Indonesian waters and the Indian Ocean, were reviewed.
The estimated Japanese longline catches from the South China Sea attained their peak of about 6,800 tons in 1967 and since then they have fluctuated between 2,000 and 5,000 tons with somewhat downward trend. The yellowfin and bigeye tuna accounted for ninety percent of the Japanese catch more. The remainder was occupied by the billfish, mostly the blue marlin and black marlin. The total longline catch by the Japanese and Taiwanese fisheries from the South China Sea area were roughly estimated to be between 5,000 and 8,000 tons in a recent few years.
Among the small-sized tuna and tuna-like fishes, the skipjack, little tuna, longtail tuna, frigate mackerel and bonito seemed to be promising for their future exploitation. The biological information on some of them was briefly reviewed.
Recent activities in research on tuna fisheries in the Indo-Pacific areas (IPFC area) have been fully reviewed by Suda (1971). For the South China Sea area, however, little has been reported on the biology of large-sized tuna except a few studies (Nakamura, 1953), although this area has long supported the tuna longline fleets from Taiwan and Japan. The purposes of this paper are: (1) to show the distribution of tunas and billfishes caught by the Japanese commercial longline fishery in the South China Sea and its adjacent waters on the past data, (2) to show the recent trend in the longline catches from these areas and (3) to make a short review on the occurrence of small-sized tuna and tuna-like fishes in Southeast Asian waters. | en |
| dc.language.iso | en | en |
| dc.publisher | Japan International Cooperation Agency | en |
| dc.subject | Thunnus albacares | |
| dc.subject | Thunnus obesus | |
| dc.subject | Thunnus alalunga | |
| dc.subject | Thunnus thynnus | |
| dc.subject | Istiophorus platypterus | |
| dc.subject | Tetrapturus angustirostris | |
| dc.subject | Kajikia audax | |
| dc.subject | Makaira nigricans | |
| dc.subject | Makaira mazara | |
| dc.subject | Makaira indica | |
| dc.subject | Xiphias gladius | |
| dc.subject | Katsuwonus pelamis | |
| dc.subject | South China Sea | en |
| dc.title | Tuna and tuna-like fish resources in the South China Sea and adjacent waters | en |
| dc.type | Conference paper | en |
| dc.citation.spage | 31 | |
| dc.citation.epage | 41 | |
| dc.subject.asfa | tuna fisheries | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | finfish fisheries | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | marine fisheries | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | pelagic fisheries | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | commercial species | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | longlining | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | size distribution | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | seasonal distribution | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | geographical distribution | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | fishing effort | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | check lists | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | natural resources | en |
| dc.citation.conferenceTitle | Proceedings of the Technical Seminar on South China Sea Fisheries Resources, Bangkok, Thailand, 21-25 May 1973 | en |