Perlihatkan publikasi sederhana
Principles of fish farm establishment: Site selection, pond/cage design and development
Share
| dc.contributor.author | Choomthi, Arkom | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-03-26T06:05:14Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-03-26T06:05:14Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2008 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Choomthi, A. (2008). Principles of fish farm establishment: Site selection, pond/cage design and development. In Handbook on Community-based Aquaculture for Remote Rural Areas of Southeast Asia (pp. 16-25). Bangkok, Thailand: Secretariat, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center. | en |
| dc.identifier.isbn | 9789741387359 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12066/4645 | |
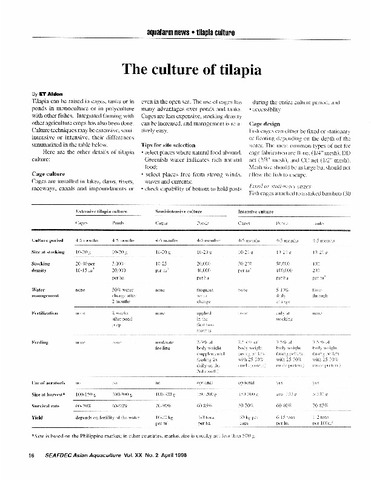
| dc.description.abstract | Fish farming is the principal form of aquaculture. It involves raising fish efficiently in ponds tanks, cages or enclosures, usually for food. A facility that releases juvenile fish into the wild for recreational fishing or to supplement for culture is generally referred to as a fish hatchery. Fish are excellent animals to rear. They can convert feed into body tissue more than most farm animals, transforming about 70 percent of their feed into flesh. Fish also have excellent dress-out qualities, providing an average of 60 percent body weight as marketable product and a greater proportion of edible, lean tissue than most livestock. Fish can be intensively cultured in relatively small amounts of water. They can be farmed at densities with careful management. Increasing demands on wild fisheries by commercial fishing operations have caused widespread overfishing. Fish farming offers an alternative solution to the increasing market demand for fish and fish protein. [Extract] | en |
| dc.publisher | Secretariat, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center | en |
| dc.relation.ispartofseries | SEC/SP/90 | en |
| dc.subject | South East Asia | en |
| dc.subject | cages | en |
| dc.subject | hatcheries | en |
| dc.title | Principles of fish farm establishment: Site selection, pond/cage design and development | en |
| dc.type | Book chapter | en |
| dc.citation.spage | 16 | |
| dc.citation.epage | 25 | |
| dc.subject.asfa | fish culture | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | aquaculture | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | site selection | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | pond construction | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | ponds | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | water quality | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | soil | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | water supply | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | breeding stock | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | breeding sites | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | juveniles | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | sustainability | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | sustainable fishing | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | pond culture | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | cage culture | en |
| dc.citation.bookTitle | Handbook on Community-based Aquaculture for Remote Rural Areas of Southeast Asia | en |