Water quality assessment of the Langat River, Selangor, Malaysia using the natural algal periphyton community and laboratory bioassays of two Chlorella species
Share
Abstract
The physico-chemical conditions in 10 sampling stations off the headwaters of the Langat River, Selangor, Malaysia were studied. Monitoring was done twice a month from June to December 1980. Changes in water quality were observed downstream. A total of 35 taxa of periphyton in four main divisions of algae were identified. The decrease in the number of species in downstream stations could be due to changes in the river rather than to chemical pollution. Two species of Chlorella , namely, C. pyrenoidosa and C. vulgaris , were grown in filtered river water obtained from the different sampling stations to assess their growth responses. Results suggest that pollution in the Langat River was caused mainly by heavy siltation rather than chemical pollutants.
Suggested Citation
Anton, A. (1990). Water quality assessment of the Langat River, Selangor, Malaysia using the natural algal periphyton community and laboratory bioassays of two Chlorella species. In I. J. Dogma Jr., G. C. Trono Jr., & R. A. Tabbada (Eds.), Culture and use of algae in Southeast Asia: Proceedings of the Symposium on Culture and Utilization of Algae in Southeast Asia, 8-11 December 1981, Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines. (pp. 51-54). Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines: Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center.
Subject
Collections
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Mercury levels in the sediment, water, and selected finfishes of Laguna Lake, the Philippines
Cuvin-Aralar, Maria Lourdes A. (Elsevier, 1990)Monthly samples of sediment, water and commercially important species of fish, primarily Oreochromis niloticus and Chanos chanos , plus a few other species, were collected from the West Bay area of Laguna Lake, The Philippines ... -
Integrating effluent management
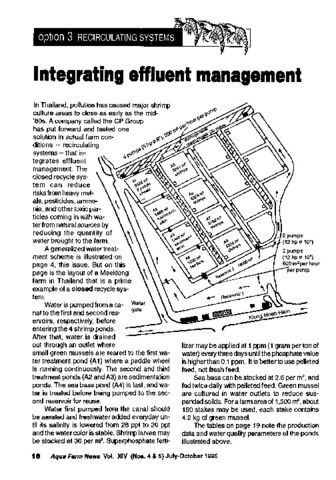
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1996)The paper discusses a closed recycle shrimp farm in Thailand which integrates effluent management. The closed recycle system can reduce risk of heavy metals, pesticides, ammonia, and other toxic particles coming in with ... -
Public health aspects: Molluscs as food
Castaños, Milagros T.; Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1992)