Polyculture of green mussels, brown mussels and oysters with shrimp control luminous bacterial disease in a simulated culture system

Lihat/Open
Tarikh
2007Pengarang
Page views
790Metadata
Lihat penerbitan penuhCited times in Scopus
- Citations
- CrossRef - Citation Indexes: 12
- Patent Families - Patent Family Citations: 1
- Policy Citation - Policy Citations: 2
- Scopus - Citation Indexes: 26
- Captures
- Mendeley - Readers: 57
Share
abstrak
Shrimp mortality due to luminous bacteria has been a problem of the shrimp industry worldwide. Polyculture of shrimp with finfish, such as grouper, seabass, snapper, siganid, Tilapia hornorum, and the Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (GIFT), could control the growth of luminous bacteria. One way to reduce adverse environmental impact and to reduce bacterial count is through the use of bivalves to filter pond effluents.
This study investigated the effect of several bivalves on the growth of luminous bacteria in a simulated shrimp culture environment using concrete tanks. Tanks were stocked with shrimp at a biomass of 100 g/m3 and with brown mussel (158 pcs/m3), green mussel (137 pcs/m3), or oyster (376 pcs/m3). Growth of luminous bacteria decreased to below 101 cfu/ml in tanks with green mussel after 5 d, brown mussel after 16 d, and oyster after 17 d. Bivalves, such as green and brown mussels, and oyster, could be used as an alternative species for polyculture with shrimp to control disease due to luminous bacteria.
Suggested Citation
Tendencia, E. (2007). Polyculture of green mussels, brown mussels and oysters with shrimp control luminous bacterial disease in a simulated culture system. Aquaculture , 272(1-4), 188-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.07.212
Subjek
Taxonomic term
Koleksi
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Impact of seafarming: Fish farms vs. mussel farms
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1994)The article presents comparative impacts of fish and mussel seafarms. Specifically, it tackles about the impacts of the two farms on the following: solid waste production, water flow and sedimentation, effect on native ... -
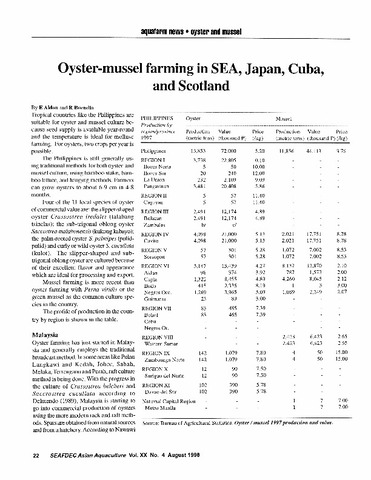
Oyster-mussel farming in SEA, Japan, Cuba, and Scotland
Aldon, Eva; Buendia, Romeo (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998) -
The different ways to grow oysters and mussels
Aldon, Eva T. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)