Linoleic (ω6) and linolenic (ω3) acids in the diet of fingerling milkfish (Chanos chanos Forsskal)
Share
Abstract
Feeding trials were conducted to determine the effects of linoleic acids on growth, survival, fatty acid composition and liver histology of milkfish. Five isocaloric semi-purified diets were formulated, either lipid-free or containing the following lipids: 7% lauric acid (LA), 6% LA + 1% linoleic, 6% LA + 1% linolenic acid, and 6% LA + 0.5% linoleic + 0.05% linolenic acids, and fed to milkfish with an average weight of 1.55 ± 0.25 g. there were no significant differences in growth or survival between fish fed the lipid-free and the LA diets in the five treatments tested. However, growth of fish fed with linoleic and linolenic acids was significantly higher (P<0.05) than that obtained in fish fed lipid-free and LA diets. The best growth response (233%) was attained with fish fed linolenic acid alone. Fatty acid analyses of the total lipid showed that lipid-free and LA diets increased the levels of monoenoic acids in the fish. The addition of linoleic and linolenic acids, alone or in combination, suppressed the levels of these monoenes and increased the levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). Histological analyses using light microscopy revealed slight abnormalities in the hepatocytes of fish fed lipid-free and LA diets. Both linoleic and linolenic acids are effective for good growth and survival of fingerling milkfish; however, the effect of linolenic acid on the growth of this species is better than that of linoleic acid.
Suggested Citation
Teruel, M. B., & de la Cruz, M. C. (1988). Linoleic (ω6) and linolenic (ω3) acids in the diet of fingerling milkfish (Chanos chanos Forsskal). Aquaculture , 71(4), 347-358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(88)90204-9
Subject
Taxonomic term
Koleksi
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Small-scale freshwater aquaculture development: Experiences from the Philippines on giant freshwater prawn, milkfish and tilapia
Aya, Frolan (Japan International Cooperation Agency, 2013-12)The Aquaculture Department of the Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC/AQD) has been promoting a number of programs towards effective dissemination and adoption of science-based aquaculture technologies ... -
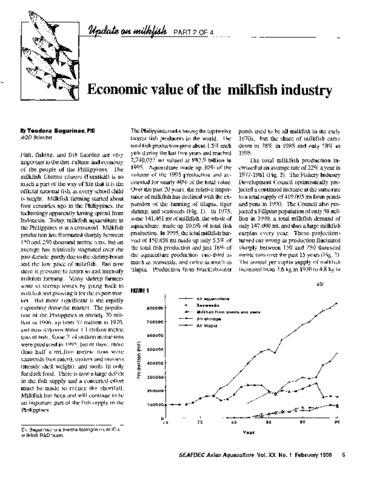
Economic value of the milkfish industry
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)A brief description is given of the milkfish (Chanos chanos) farming industry in the Philippines. Over the past 20 years, the relative importance of milkfish has declined with the expansion of tilapia, tiger shrimp and ... -
Milkfish ponds from mangroves
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)