A survey of chemical and biological products used in intensive prawn farms in the Philippines
Share
Abstract
With attractive prawn export prices and the availability of hatchery fry and commercial feeds, Philippine aquaculture has experienced a shift from milkfish to prawn Penaeus monodon and an intensification from traditional and extensive prawn culture to higher stocking densities. This paper features the results of a survey of intensive prawn farms (n = 21) in Western Visayas and Northern Mindanao conducted in 1990. Average farm size, production, feeding and water management are described. To solve the self-pollution characteristic of intensive ponds, the farms utilized some 40 chemical and biological products; at least another 35 were available in the market at the time of the study. These include therapeutants and disinfectants, soil conditioners, bacteria-enzyme preparations, algicides and piscicides, plankton growth promoters, and feed additives. The possible ecological effects of effluents drained into adjacent marine waters are discussed; some recommendations are given.
Suggested Citation
Primavera, J., Lavilla-Pitogo, C. R., Ladja, J. M., & de la Peña, M. R. (1993). A survey of chemical and biological products used in intensive prawn farms in the Philippines. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 26(1), 35-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(93)90595-B
Subject
Taxonomic term
Collections
- AQD Journal Articles [1248]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
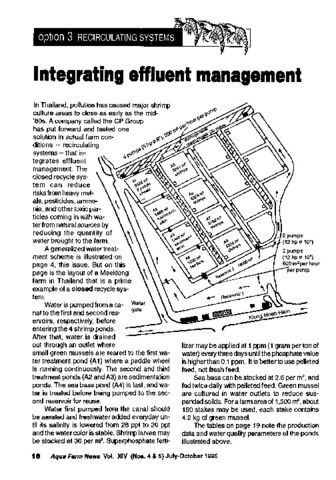
Integrating effluent management
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1996)The paper discusses a closed recycle shrimp farm in Thailand which integrates effluent management. The closed recycle system can reduce risk of heavy metals, pesticides, ammonia, and other toxic particles coming in with ... -
Chemicals in Asian aquaculture: need, usage, issues and challenges
Subasinghe, Rohana P.; Barg, Uwe; Tacon, Albert (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 2000)This paper outlines the opening introductory presentation made at the “Expert Meeting on the Use of Chemicals in Aquaculture in Asia,” which was held 20-22 May 1996 at the SEAFDEC facilities in Tigbauan, Iloilo, the ... -
Ecological effects of the use of chemicals in aquaculture
Weston, Donald P. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 2000)Many aquaculture chemicals are, by their very nature, biocidal, and may be released to the surrounding environment at toxic concentrations either through misuse, or in some cases, even by following generally accepted ...