| dc.description.abstract | The rapid population decline of temperate eels and the listing of some anguillid eel species, i.e. Anguilla anguilla and A. japonica in the CITES Appendices, have led to the increase in the market value of tropical eels during the recent years. European, American, and Japanese eels are seriously threatened with extinction due to high consumption, and demand is still increasing. After the stocks and recruitment collapse in the present target eel species and areas, it has to seek other targets for replacement and compensation to continue eel consumption (Arai, 2015). Since 2009, CITES for international trade listed the European eel in Appendix II due to their decreasing population and potential extinction. In East Asia, the large consumption of the Japonica eel has led to a rapid decline in the number of glass eels. Moreover, the demand for tropical anguillid eels in Southeast Asia has increased, not only for domestic consumption but also mainly for export to East Asian countries. Since the Japanese eels and European eels are under the control of the IUCN, the development of sustainable anguillid eel fisheries could be an excellent prospect to increase the source of income of small-scale fishers in Southeast Asia.
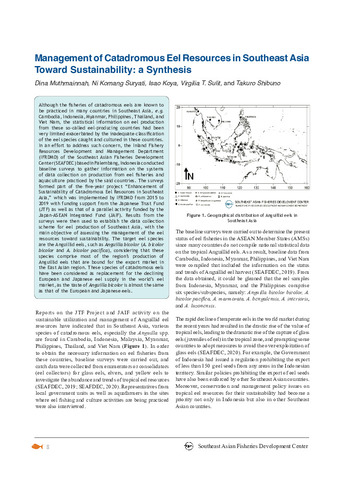
SEAFDEC conducted the studies to obtain a better understanding of the status, biology, and life cycle of eel stocks and promote sustainable management and utilization of anguillid eel fishery resources in the region. To better understand the stock status, biology, and life cycle of eel stocks and promote sustainable management and utilization of anguillid eel fisheries resources in the region, SEAFDEC carried out two projects, namely: “Development of Stock Assessment Methods and Strengthening of Resources Management Measures for Tropical Anguillid Eel in Southeast Asia” in 2020–2022 and “Sustainable Utilization of Anguillid Eels in the Southeast Asia Region” in 2020–2024. The former Project was implemented by the SEAFDEC Secretariat in collaboration with IFRDMD with funding support from the Japan-ASEAN Integration Fund (JAIF) with the aims to collect catch data and biological/ecological information for the estimation of eel resources stocks and develop methods for estimating tropical anguillid eel resources. While the latter Project was implemented by IFRDMD with funding support from Japan Trust Fund VI (JTF) Phase 2 with the aim of keeping the sustainable management and utilization of anguillid eel fisheries resources in the Southeast Asian region through the strategic program of sustainable eel resources management. The anguillid eels are common in several ASEAN Member States (AMSs), namely: Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand, and Viet Nam. This article presents the capture fishery practices for anguillid eels in the AMSs and the national fishery management programs and regulations implemented by the respective countries to sustain the utilization of eel resources in the region. | en |