Viability of milkfish eggs and larvae after simulated and actual transport
Share
Abstract
The viability of milkfish eggs and larvae after simulated and actual transport was investigated. Naturally-spawned milkfish eggs were collected and subjected to simulated or actual transport at early cleavage stage (stage 1), blastula (stage 2), gastrula (stage 3), "eyed" (stage 4), or newly-hatched larvae (stage 5). Replicate samples in aerated plastic jars served as controls. Mean hatching and survival rates and the percentage of newly-hatched larvae were significantly affected by the modes of transport and by the stage of embryonic development at transport. Eggs transported at the 'eyed' stage had higher viability compared to those transported at cleavage, blastula, or gastrula stages. There was no significant difference in the mean survival rate of the larvae after 26 days of rearing. However, the percentage of 45 day old larvae with apparent morphological abnormalities was lower in groups transported at stages 4 and 5. These observations indicate that milkfish eggs should be handled and transported during the late embryonic stages to minimize mortalities and the incidence of abnormalities in larvae.
Suggested Citation
Toledo, J. D., Doi, M., & Duray, M. (1996). Viability of milkfish eggs and larvae after simulated and actual transport. In D. MacKinlay & M. Eldridge (Eds.), The Fish Egg: Its Biology and Culture Symposium Proceedings. International Congress on the Biology of Fishes, San Francisco State University July 14-18, 1996 (pp. 51–58). Physiology Section, American Fisheries Society.
Subject
Taxonomic term
Collections
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Small-scale freshwater aquaculture development: Experiences from the Philippines on giant freshwater prawn, milkfish and tilapia
Aya, Frolan (Japan International Cooperation Agency, 2013-12)The Aquaculture Department of the Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC/AQD) has been promoting a number of programs towards effective dissemination and adoption of science-based aquaculture technologies ... -
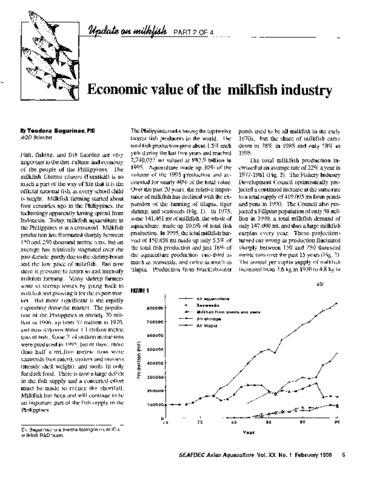
Economic value of the milkfish industry
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)A brief description is given of the milkfish (Chanos chanos) farming industry in the Philippines. Over the past 20 years, the relative importance of milkfish has declined with the expansion of tilapia, tiger shrimp and ... -
Milkfish ponds from mangroves
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)