Effects of dietary lipid source on reproductive performance and tissue lipid levels of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus) broodstock
Share
Abstract
Nile tilapia were fed diets supplemented with one of the following lipid sources at 5% level: cod liver oil, corn oil, soybean oil, a coconut oil-based cooking oil or a combination of cod liver oil and corn oil (1 : 1). The control diet had no lipid supplement and tad fish meal as a sole protein source. A diet with soybean meal as a protein source was also tested. The number of females that spawned, spawning frequency, number of fry per spawning, and total fry production were increased at varying degrees by the supplemental lipid sources except for the cod liver oil. Fish fed the soybean oil diet tad the best overall reproductive performance over a 24-week period. Fish fed the cod liver oil diet had the highest weight gain but the poorest reproductive performance. The suplemental lipids significantly increased crude fat levels in the liver and ovaries. Both males and females Ld the cod liver oil diet had the highest levels of fat in the liver and muscle. The ratio of total n-6/n-3 fatty acid in the liver, ovaries and testes was influenced by the supplemental lipid sources. It was highest in fish fed either the soybean oil diet, the corn oil diet, or the soybean meal diet and lowest in fish fed the control diet or the cod liver oil diet.
Suggested Citation
Santiago, C. B., & Reyes, O. S. (1993). Effects of dietary lipid source on reproductive performance and tissue lipid levels of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus) broodstock. Journal of Applied Ichthyology , 9(1), 33-40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.1993.tb00385.x
Subject
Collections
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
The essential nutrients: Lipids and fatty acids
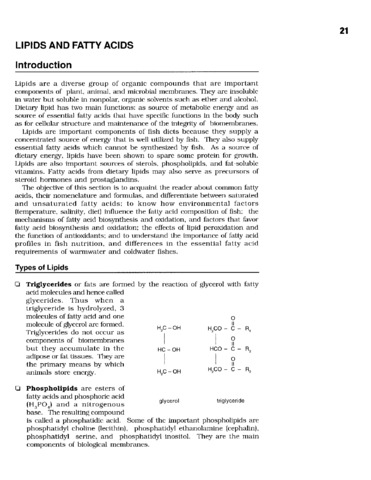
Millamena, Oseni M. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 2002)The objective of this section is to acquaint the reader about common fatty acids, their nomenclature and formulas, and differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids; to know how environmental factors (temperature, ... -
Effect of supplemental lecithin and lipid sources on the growth and survival of Penaeus monodon juveniles
Piedad-Pascual, Felicitas. (Asian Fisheries Society, 1986)Penaeus monodon juveniles were reared in 60-liter fiberglass oval tanks in a flow-through seawater system for 8 weeks to determine the effect of lecithin and type of lipid on growth and survival. Nine isonitrogenous and ... -
Lipid composition of milkfish grown in ponds by traditional aquaculture
Benitez, Lita V.; Gorriceta, Ilda R. (International Development Research Centre, 1985)Milkfish is one of the most important food fish in the Southeast Asia. It is widely cultured in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Taiwan(Chen 1976). In the Philippines, about 90% of the total aquaculture production comes ...