Effect of detention time on aerobic waste stabilization pond performance in Southeast Asia
Share
Abstract
The rising level of pollution in rivers, lakes and other bodies of water has created problems of significant magnitude in Southeast Asia. Apart from the aesthetic desirability of clean rivers are the pressing dangers to health and detrimental effects on aquatic life. Pollution of these sources must be controlled so as not to interfere with the waters' legitimate uses.
Waste stabilization ponds are well-accepted as an effective and economical means of waste disposal. A "stabilization pond" is an artificially created body of water intended to retain sewage or organic wastes until biological processes have rendered the wastes stable. The stabilization process consists of bacteria and algae interaction. Bacteria oxidize the wastes and produce sludge, carbon dioxide and ammonia. The nutrients produced from bacterial oxidation, along with light energy, supply the requirements for algal photosynthesis. Algae produce oxygen needed to sustain the treatment process. Optimum detention time refers to the average length of time required for waste to become stabilized within a pond.
Properly designed and operated, a stabilization pond can provide treatment comparable to a more costly waste treatment plant. However, the design criteria for a particular climate may not be applicable to other climates. This study was conducted to establish suitable detention times for aerobic stabilization ponds in Southeast Asia.
Suggested Citation
Millamena, O. M. (1994). Effect of detention time on aerobic waste stabilization pond performance in Southeast Asia. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology , 52(6), 856-863. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200694
Subject
Collections
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Mercury levels in the sediment, water, and selected finfishes of Laguna Lake, the Philippines
Cuvin-Aralar, Maria Lourdes A. (Elsevier, 1990)Monthly samples of sediment, water and commercially important species of fish, primarily Oreochromis niloticus and Chanos chanos , plus a few other species, were collected from the West Bay area of Laguna Lake, The Philippines ... -
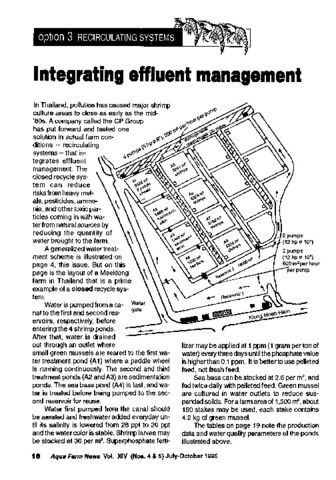
Integrating effluent management
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1996)The paper discusses a closed recycle shrimp farm in Thailand which integrates effluent management. The closed recycle system can reduce risk of heavy metals, pesticides, ammonia, and other toxic particles coming in with ... -
Public health aspects: Molluscs as food
Castaños, Milagros T.; Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1992)