| dc.contributor.author | Lebata, Ma. Junemie Hazel L. | |
| dc.coverage.spatial | Estancia | en |
| dc.coverage.spatial | Iloilo | en |
| dc.coverage.spatial | Philippines | en |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-09-21T08:38:08Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-09-21T08:38:08Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2001 | |
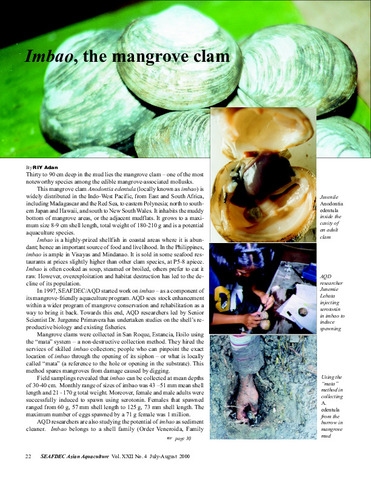
| dc.identifier.citation | Lebata, M. J. H. L. (2001). Oxygen, sulphide and nutrient uptake of the mangrove mud Clam Anodontia edentula (Family: Lucinidae). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(11), 1133–1138. | en |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0025-326X | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10862/1670 | |
| dc.description.abstract | Oxygen, sulphide and nutrient (ammonia, nitrite and phosphate) uptake of Anodontia edentula was measured. Oxygen and sulphide were measured from sealed containers provided with 1 l fresh mangrove mud (sulphide source) and seawater (oxygen source) with two treatments (with and without clam) at 16 replicates each. Oxygen, sulphide and other parameters were measured at days 1 (initial), 3 and 5 (final). Nutrients were measured from containers filled with 1.5 l wastewater from a milkfish broodstock tank with two treatments (with and without clam) at eight replicates each. Ammonia, NO2 and PO4 were measured at days 0 (initial) 3, 6, 9 and 12 (final). Results showed significantly decreasing oxygen and sulphide concentrations in treatment with clams (ANOVA, p < 0.001). A significantly higher ammonia concentration (ANOVA, p < 0.05) was observed in treatment with clams while no significant difference was observed in nitrite and phosphate between the two treatments. A decreasing ammonia and an increasing nitrite trend was also observed in both treatments starting at day 3. | en |
| dc.language.iso | en | en |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier | en |
| dc.subject | Lucinidae | en |
| dc.subject | Anodontia edentula | en |
| dc.subject | Philippines | en |
| dc.title | Oxygen, sulphide and nutrient uptake of the mangrove mud clam Anodontia edentula (Family: Lucinidae) | en |
| dc.type | Article | en |
| dc.citation.volume | 42 | |
| dc.citation.issue | 11 | |
| dc.citation.spage | 1133 | |
| dc.citation.epage | 1138 | |
| dc.citation.journalTitle | Marine Pollution Bulletin | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | oxygen consumption | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | sulphides | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | sediment pollution | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | phosphates | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | bioaccumulation | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | nitrites | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | brackishwater pollution | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | ammonia | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | mangrove swamps | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | biological uptake | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | marine molluscs | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | oxygen | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | marine pollution | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | marine environment | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | mineral nutrients | en |
| dc.subject.asfa | mangroves | en |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00113-8 | |
| dc.subject.scientificName | Anodontia edentula | |
| local.subject | Anodontia edentula | en |
| local.subject | Philippines | en |
| local.subject | ammonia | en |
| local.subject | nitrite | en |
| local.subject | phosphate | en |
| local.subject | sulphide | en |
| local.subject | imbao | hil |