Milkfish breeding program in the Philippines
Share
abstrak
The National Bangus Breeding Project (NBBP) was established in 1981 in compliance with a presidential directive. Breeding and hatchery techniques for milkfish (Chanos chanos) developed by the Aquaculture Department of the Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC/AQD) are adopted. The project is a joint undertaking of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR) of the Department of Agriculture and SEAFDEC/ AQD with the former as the lead implementing agency.
Suggested Citation
Arevalo, N. B. (1993). Milkfish breeding program in the Philippines. In C. T. Villegas, M. T. Castaños, & R. B. Lacierda (Eds.), Proceedings of the Aquaculture Workshop for SEAFDEC/AQD Training Alumni, 8-11 September 1992, Iloilo, Philippines (pp. 13-20). Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines: Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center.
Subjek
Taxonomic term
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Small-scale freshwater aquaculture development: Experiences from the Philippines on giant freshwater prawn, milkfish and tilapia
Aya, Frolan (Japan International Cooperation Agency, 2013-12)The Aquaculture Department of the Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC/AQD) has been promoting a number of programs towards effective dissemination and adoption of science-based aquaculture technologies ... -
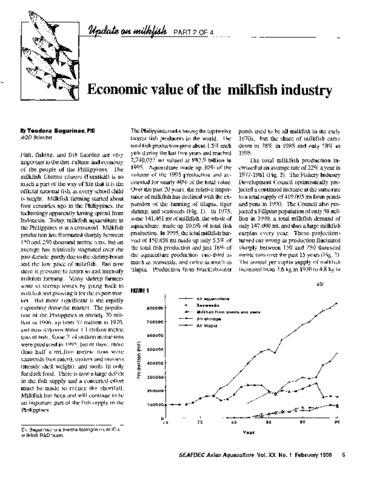
Economic value of the milkfish industry
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)A brief description is given of the milkfish (Chanos chanos) farming industry in the Philippines. Over the past 20 years, the relative importance of milkfish has declined with the expansion of tilapia, tiger shrimp and ... -
Milkfish ponds from mangroves
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)