Growth, daily ration, and gastric evacuation rates of milkfish (Chanos chanos) fed supplemental diet and natural food
Share
Abstract
Growth, daily ration, and gastric evacuation rates of milkfish (Chanos chanos) that fed on natural food and supplement diet were evaluated. Milkfish fingerlings (5.5g) were stocked at 1.5 fish/m2 in ten 12 m2 concrete tanks layered with 15-cm thick earthen bottoms. All tanks were regularly fertilized (16–20–0 and chicken manure) to maintain natural food production; 4 of the tanks additionally received a supplemental diet containing 34.3% protein and 4290 kcal/kg gross energy. Estimates or daily ration (based on dry weight of stomach contents) were calculated using the Elliot and Person (1978) and Eggers 1977) models. Gastric evacuation rate was lower in fish that fed on natural food (1.57) compared to fish fed a supplemental diet (1.79). Consequently, the lower rate resulted in lower food intake and slower fish growth. When fish were provided a high quality supplemental diet, daily rations for fingerlings (35 g) to marketable size (116 g) ranged approximately from 0.60 to 19.68 kcal/fish/day. The deviation in daily ration (kcal/fish/day) from the above estimates may indicate the insufficient quantity of dietary energy taken by fish from natural food alone, which could be provided by supplemental diet.
Suggested Citation
Sumagaysay, N. S. (1993). Growth, daily ration, and gastric evacuation rates of milkfish (Chanos chanos) fed supplemental diet and natural food. Journal of Applied Ichthyology , 9(2), 65-73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.1993.tb00527.x
Subject
Taxonomic term
Collections
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Small-scale freshwater aquaculture development: Experiences from the Philippines on giant freshwater prawn, milkfish and tilapia
Aya, Frolan (Japan International Cooperation Agency, 2013-12)The Aquaculture Department of the Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC/AQD) has been promoting a number of programs towards effective dissemination and adoption of science-based aquaculture technologies ... -
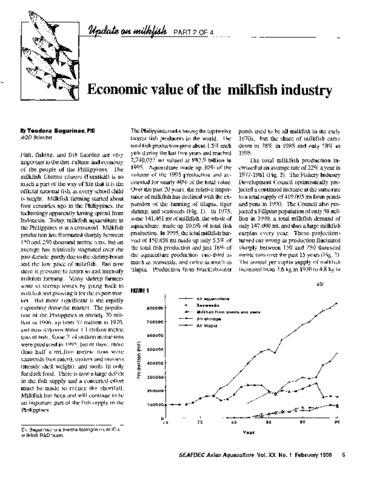
Economic value of the milkfish industry
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)A brief description is given of the milkfish (Chanos chanos) farming industry in the Philippines. Over the past 20 years, the relative importance of milkfish has declined with the expansion of tilapia, tiger shrimp and ... -
Milkfish ponds from mangroves
Bagarinao, Teodora (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1998)