Diet composition, feed preferences and mouth morphology of early stage silver therapon (Leiopotherapon plumbeus, Kner 1864) larvae reared in outdoor tanks

Quan điểm/
Ngày
2015Page views
587metadata
Hiển thị bản ghi đầy đủ mặt hàngCited times in Scopus
Share
trừu tượng
This study examined the diet composition, feeding preferences, and mouth morphology of the silver therapon (Leiopotherapon plumbeus, Kner 1864) larvae under captive conditions. Larvae were reared in outdoor tanks (4 m3) with natural food grown 2 weeks prior to start of larval rearing. Food preference was measured by the Chesson's electivity index (αi). Gut content analysis of larvae sampled between 5 and 25 days after hatching (DAH) showed the dominance in the diet by zooplankton, mainly copepod nauplii, cladocerans and insect larvae. Small fish larvae (5–9 DAH; 3.32–6.29 mm standard length) preferred cladocerans, ciliates and copepod nauplii; whereas older larvae (12–25 DAH; 5.45–19.26 mm standard length) preferred insect larvae over cladocerans and adult insects. The mouth gape size at 5 DAH was 359 μm and increased to 3.75 mm at 40 DAH when body size grew at an average rate of 0.59 mm d−1. The standard length (SL) of L. plumbeus larvae was strongly associated with mouth size (r2 = 0.98, P < 0.05), indicating a progressive increase of ingested prey size of the fish larvae. These results clarified the early life feeding ecology of this species, which is essential in developing effective hatchery techniques.
Suggested Citation
Aya, F., Corpuz, M. N. C., & Garcia, L. M. (2015). Diet composition, feed preferences and mouth morphology of early stage silver therapon (Leiopotherapon plumbeus, Kner 1864) larvae reared in outdoor tanks. Journal of Applied Ichthyology , 31(1), 77-82. https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.12486
Chủ thể
plankton surveys  ; animal morphology
; animal morphology  ; insect larvae
; insect larvae  ; length
; length  ; food preferences
; food preferences  ; biometrics
; biometrics  ; nutrition
; nutrition  ; fish larvae
; fish larvae  ; protists
; protists  ; diet
; diet  ; feeding
; feeding  ; zooplankton
; zooplankton  ; stomach content
; stomach content  ; hatcheries
; hatcheries  ; digestive system
; digestive system  ; body size
; body size  ; mouth
; mouth  ; hatching
; hatching  ; predation
; predation  ; Copepoda
; Copepoda  ; Cladocera
; Cladocera  ; Ciliophora
; Ciliophora 
 ; animal morphology
; animal morphology  ; insect larvae
; insect larvae  ; length
; length  ; food preferences
; food preferences  ; biometrics
; biometrics  ; nutrition
; nutrition  ; fish larvae
; fish larvae  ; protists
; protists  ; diet
; diet  ; feeding
; feeding  ; zooplankton
; zooplankton  ; stomach content
; stomach content  ; hatcheries
; hatcheries  ; digestive system
; digestive system  ; body size
; body size  ; mouth
; mouth  ; hatching
; hatching  ; predation
; predation  ; Copepoda
; Copepoda  ; Cladocera
; Cladocera  ; Ciliophora
; Ciliophora 
Taxonomic term
Bộ sưu tập
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Successful use of cryopreserved oyster trocophores as a live first feed larval marine fish and invertebrates
Harvey, Brian J. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1996)Trochophore-stage larvae of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas were cryopreserved in bulk and stored in liquid nitrogen for periods up to two years before thawing and feeding to a variety of warmwater and coldwater larval ... -
Larviculture of marine species in Southeast Asia: current research and industry prospects
Marte, Clarissa L. (Elsevier, 2003)The increased requirement for food fish, the lucrative market for expensive seafood, and the need to conserve marine resources, have motivated the rapid pace of larviculture research in Southeast Asia. Various research and ... -
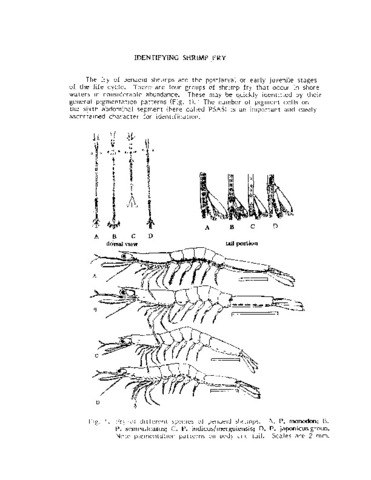
Identifying shrimp fry
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1988)