Metabolic rate characteristics and sediment cleaning potential of the tropical sea cucumber Holothuria scabra
Share
abstrak
The oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and ammonium excretion rate (AER) of a tropical sea cucumber, Holothuria scabra, were determined in laboratory experiments. OCR and AER exhibited a significant negative correlation to body weight (BW), expressed as a power function of \(\mathrm{BW:}\; \mathit{OCR} = 0.09 \times BW^{-0.58}(\mathrm{mgO_{2}/g/h, r^{2}=0.89, n=15})\) and \(AER = 0.38 \times BW^{-0.19}\) \((\mathrm{\mu\text{molN/g/h}}, \mathrm{r^{2}=0.54}, n=15)\). These values were comparable to those in previous studies on other sea cucumber species. The OCR of shrimp tank sediment was reduced to less than half \((4.5 \pm 0.3 \mathrm{\;to\;} 1.0 \pm 0.1\;\mathrm{mgO_{2}/gdry/h)}\) by the ingestion and excretion process of H. scabra. Acid volatile sulfide (AVS-S) concentration was also decreased to less than half (0.67 to 0.31 mgS/mgdry); despite the low reduction rates of organic carbon and nitrogen contents (0.19 to 0.14 mgC/mgdry and 0.022 to 0.019 mgN/mgdry, respectively). These results suggest that components in the sediment with high oxygen consumption potential were removed by H. scabra. These findings also provide fundamental information with which to evaluate the quantitative role of H. scabra in polyculture with shrimp.
Suggested Citation
Kodama, M., Sumbing, J. G., Lebata-Ramos, M. J. H., & Watanabe, S. (2015). Metabolic rate characteristics and sediment cleaning potential of the tropical sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly , 49(1), 79-84. https://doi.org/10.6090/jarq.49.79
Subjek
Koleksi
- AQD Journal Articles [1249]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
The essential nutrients: Energy
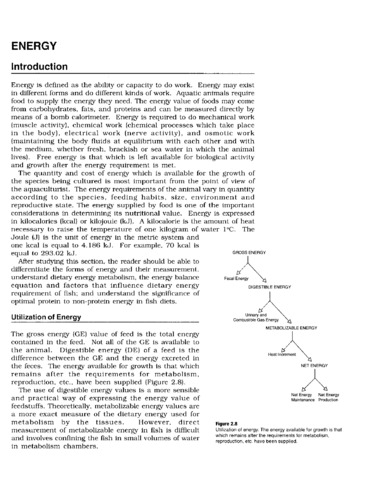
Millamena, Oseni M. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 2002)After studying this section, the reader should be able to differentiate the forms of energy and their measurement. Understand dietary energy metabolism, the energy balance equation and factors that influence dietary energy ... -
Development of transgenic fish: scientific background
Nam, Y. K.; Maclean, N.; Fu, C.; Pandian, T. J.; Eguia, Maria Rowena R. (CABI, 2007)This chapter highlights some of the important examples of transgenic fish development. An overview of important steps in fish transgenesis is given. The status of development in the case of transgenic carp, tilapias, ... -
Drug assimilation in the tissue of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fry delivered orally through bioencapsulation
Gapasin, R. S. J.; Nelis, H. J.; Chair, M.; Sorgeloos, P. (Wiley-Blackwell, 1996)Assimilation levels of the antibacterials trimethoprim (TMP) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fry tissue administered orally were investigated. A 1:5 TMP and SMX combination incorporated in an ...